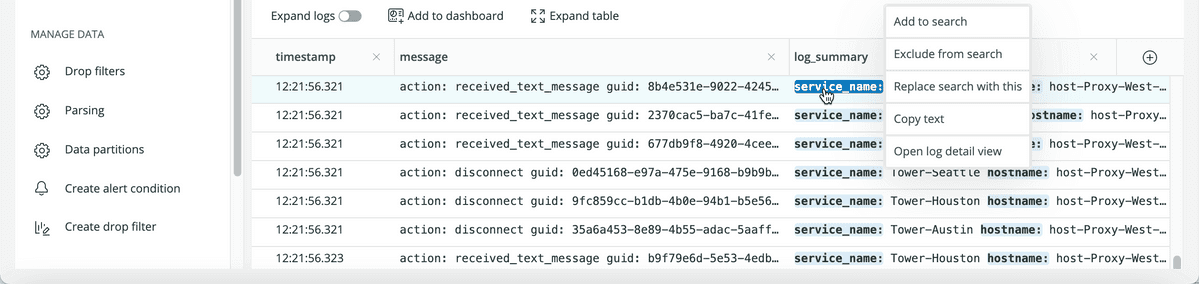
Use our Logs UI in New Relic One to quickly search through your log data in seconds. Each log lists available attributes in the log_summary column. To drill down into additional details, click any highlighted attribute.
Each log's summary in the Logs UI provides query options to add, exclude, replace, and more.
Ready to get started? If you haven't already, be sure to sign up for a New Relic account. It's free, forever.
Query structure
Using the Logs UI, you can search through your log data by entering either simple keywords, such as new and relic, or phrases such as new relic agent, directly into the search field. You can also combine keywords or phrases with operators to form more complex queries.
Tip
Log queries in New Relic are based on the Lucene query language, and any Lucene function listed in this document is supported. (If a Lucene function is not listed, we do not support it.) For some helpful examples, check out this Lucene tutorial.
General query rules:
Log query rules | Comments |
|---|---|
Case sensitive | The query syntax is case sensitive for attributes values. Attribute names are always case sensitive. Exception: Wildcard searches are case insensitive for attribute values. |
Special characters | When a term contains special characters, double-quote the term and escape the special characters using a backslash ( Example: To query for
|
Wildcard searches | You can run wildcard searches using an asterisk ( Example: |
Search with text
To return more specific query results, use text searches to join together keywords or phrases.
Text operators
The Logs query syntax accepts the following text operators:
Condition | Text operator example |
|---|---|
Matching (keyword) | Search for log results containing keywords entered separately:
|
Exact matching (phrase) | Search for log results containing the specific phrase entered:
|
Either / Or | Search for log results containing either or both of the keywords entered:
|
And | Search for log results containing both of the keywords entered:
|
* Wildcard (zero or more) | Search for log results containing both of the keywords entered, with zero or more characters between them:
|
Negation (keyword) | Search for log results that do not contain the specific keyword entered:
|
Negation (phrase) | Search for log results that do not contain the specific phrase entered.
|
Search with attributes
Use attribute searches to narrow the query results to a specific attribute or field.
General operators
The following operators can be used by all types of attributes:
Condition | General operator example |
|---|---|
Equal | Search for log results where the attribute equals the keyword specified. Example: The field
|
Does not equal | Search for log results where the attribute does not equal the keyword specified. Example: The field
|
Contains | Search for log results where the attribute contains the specified keyword. Example: The field
|
Does not contain | Search for log results where the attribute does not contain the specified keyword. Example: The field
|
Starts with | Search for log results where the attribute starts with the specified keyword specified. Example: The field
|
Ends with | Search for log results where the attribute ends with the specified keyword specified. Example: The field
|
Has | Search for log results that have the specified field. Example: Has the field
|
Missing | Search for log results that are missing the specified field. Example: Missing the field
|
Numeric operators
The following operators can only be used by numeric attributes:
Condition | Numeric operator example |
|---|---|
Greater than | Search for log results attribute matches that are greater than the given parameter. Example: The field
|
Greater than or equal to | Search for log results with attribute matches that are greater than or equal to the given parameter. Example: The field
|
Less than | Search for log results with attribute matches that are less than the given parameter. Example: The field
|
Less than or equal to | Search for log results with attribute matches that are less than or equal to the given parameter. Example: The field
|